Costs of Insulin effect nonadherence to insulin and possibly other diabetes medications
New Study Snapshot examines the nonadherence rates for diabetes at different out-of-pocket costs.
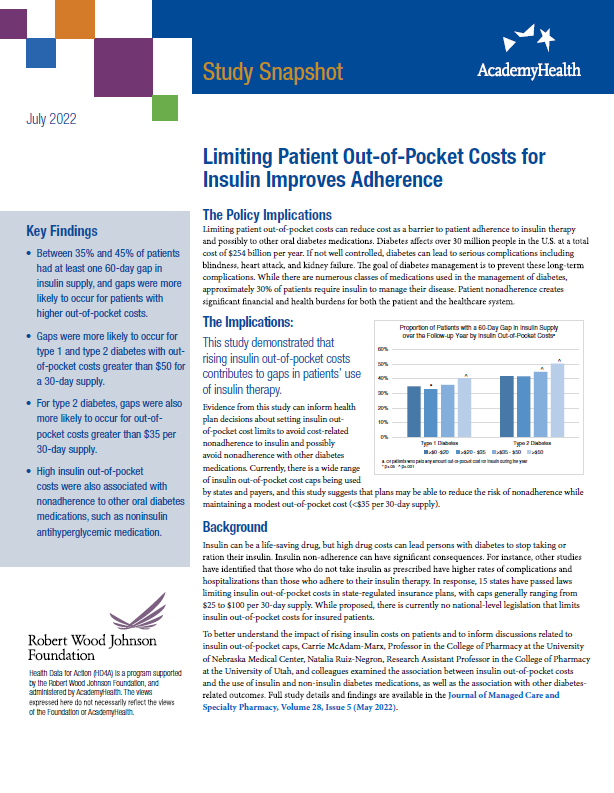
Insulin can be a life-saving drug, but high drug costs can lead persons with diabetes to stop taking or ration their insulin. Currently, there is a wide range of insulin out-of-pocket cost caps being used by states and payers.
This Study Snapshot summarizes research from Carrie McAdam-Marx, Professor in the College of Pharmacy at the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Natalia Ruiz-Negron, Research Assistant Professor in the College of Pharmacy at the University of Utah, who examined the association between insulin out-of-pocket costs and the use of insulin and non-insulin diabetes medications, as well as the association with other diabetes-related outcomes. Study findings suggest gaps in insulin adherence are likely to occur for out-of-pocket costs greater than $35 per 30-day supply.
Full findings can be found at Journal of Managed Care and Specialty Pharmacy.
This project is funded as part of the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation's Health Data for Action program, managed by AcademyHealth.